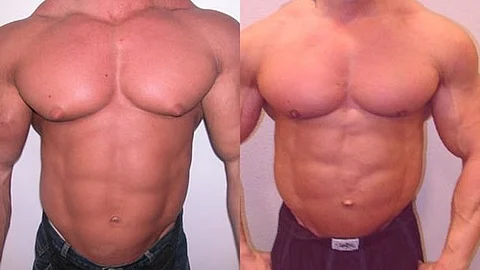
Gynecomastia surgery can dramatically improve both physical comfort and emotional well-being, but securing insurance coverage can be a lengthy and challenging journey.
By fully understanding your insurance policy, gathering detailed medical evidence, and persistently advocating for yourself, you greatly increase your odds of having the procedure covered.
Patience, organization, and clear communication between you, your healthcare providers, and your insurer are essential throughout the process. If denials occur, view them as a chance to clarify and strengthen your case, and seek outside help if necessary.
Taking these steps can help you overcome obstacles and make gynecomastia surgery more financially accessible.
MBT pg