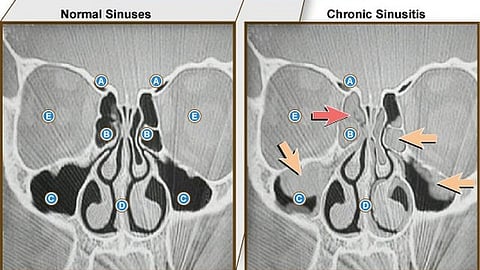
Most sinusitis are caused by viruses, sometimes bacteria and, in rare cases, fungal infections. Furthermore, sinusitis can be differentiated with regard to the affected paranasal sinuses.
In addition to conservative treatment options for chronic sinusitis (glucocorticoid nasal sprays, antibiotics, antimycotics, immunotherapy), surgical procedures (functional endoscopic sinus surgery) can also be considered. However, chronic sinusitis tends towards a high rate of recurrences. Therefore, in many cases only symptom control is achieved.